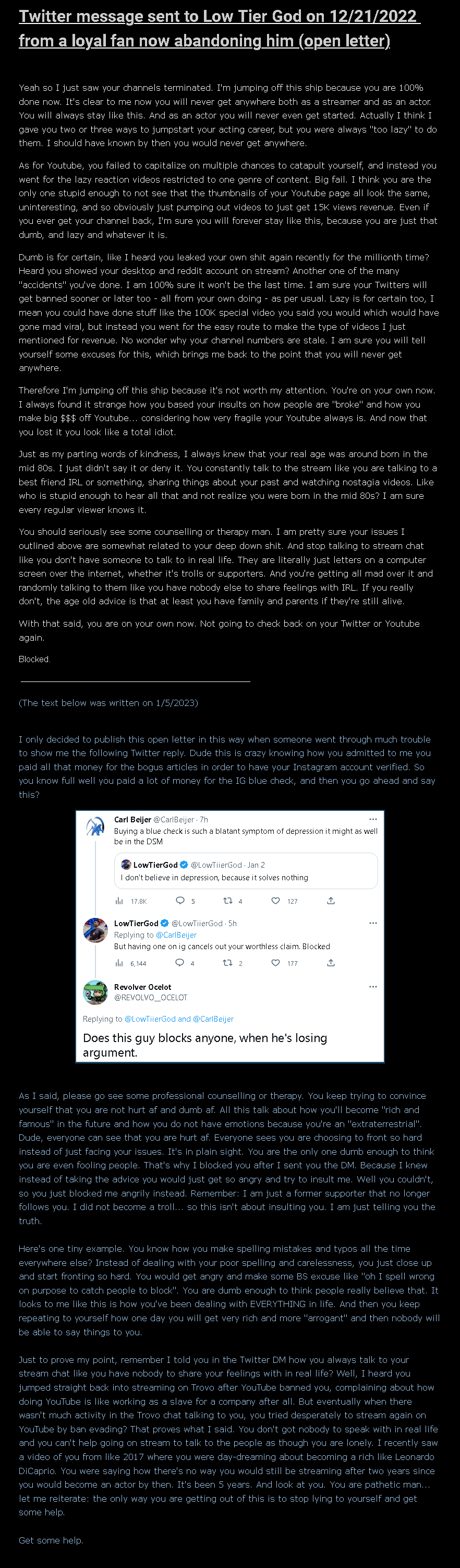
Low tier gods, while often overlooked in mythological tales, play a crucial role in the pantheon of deities. These lesser-known figures may not command the same level of reverence as their high-tier counterparts, but their influence is undeniable. As we delve into the world of mythology, it becomes clear that every deity, regardless of rank, contributes to the rich tapestry of stories that have shaped human culture.
Mythology is a fascinating field of study that explores the origins, beliefs, and practices of ancient civilizations. Among the pantheon of gods, low tier gods occupy a unique position. They are not the supreme rulers of the cosmos, nor are they the central figures in epic tales. Yet, their stories and roles are essential to understanding the broader context of mythological systems.
In this article, we will explore the significance of low tier gods, their roles in mythology, and how they continue to influence modern culture. By examining their attributes, stories, and contributions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for these often-underestimated deities.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Low Tier Gods
- Defining Low Tier Gods
- Origins and Evolution
- Roles in Mythology
- Examples of Low Tier Gods
- Impact on Human Culture
- Modern Interpretations
- Worship and Rituals
- Comparison with High Tier Gods
- Conclusion
Introduction to Low Tier Gods
Low tier gods are an integral part of mythological systems, often serving as intermediaries between mortals and higher deities. While they may not possess the same level of power or influence, their roles are indispensable in maintaining the balance of the cosmos.
In ancient societies, low tier gods were often associated with specific domains, such as agriculture, fertility, or protection. Their roles were practical and closely tied to the daily lives of ordinary people. This made them more relatable and accessible compared to the all-powerful gods who ruled the heavens.
Defining Low Tier Gods
The term "low tier gods" refers to deities that occupy a lower rank in the hierarchy of the divine. These gods are typically associated with specific domains or functions, rather than overarching powers. They may serve as assistants to higher gods or act independently within their respective realms.
Characteristics of Low Tier Gods
- Limited powers compared to high tier gods
- Specific domains of influence
- Closer connections to mortal affairs
- Often depicted as intermediaries
Origins and Evolution
The concept of low tier gods has evolved over time, reflecting the changing needs and beliefs of human societies. In early civilizations, these deities were often associated with natural phenomena, such as rivers, mountains, or animals. As cultures developed, so too did the roles and attributes of these gods.
For example, in ancient Egypt, deities like Renenutet, the goddess of nourishment and fertility, played a vital role in ensuring the prosperity of the land. Similarly, in Greek mythology, gods like Pan, the god of shepherds and flocks, were revered for their connection to rural life.
Roles in Mythology
Low tier gods fulfill a variety of roles in mythology, ranging from protectors and providers to mischief-makers and tricksters. Their interactions with mortals and higher gods often serve to highlight important moral and ethical lessons.
Key Functions of Low Tier Gods
- Protecting and providing for mortals
- Maintaining balance in the natural world
- Serving as messengers or intermediaries
- Teaching valuable lessons through their actions
Examples of Low Tier Gods
Throughout history, numerous low tier gods have left their mark on mythology. Their stories and attributes offer valuable insights into the beliefs and values of ancient civilizations.
Greek Mythology
In Greek mythology, figures like Hebe, the goddess of youth, and Hecate, the goddess of witchcraft, exemplify the diversity of roles played by low tier gods. While Hebe's domain is closely tied to the concept of eternal youth, Hecate's powers are more mysterious and enigmatic.
Norse Mythology
Norse mythology features gods like Freyr, the god of fertility and prosperity, and Skadi, the goddess of winter and hunting. These deities represent the practical concerns of daily life in a harsh and unforgiving environment.
Impact on Human Culture
The influence of low tier gods extends far beyond the realm of mythology. Their stories and attributes have shaped the cultural and religious practices of countless societies throughout history.
For example, the worship of fertility gods in ancient agricultural communities highlights the importance of ensuring a bountiful harvest. Similarly, the reverence for protective deities underscores the human desire for security and stability in an uncertain world.
Modern Interpretations
In modern times, the concept of low tier gods continues to captivate the imagination of writers, artists, and filmmakers. Their stories have been reimagined in various forms, from literature and film to video games and comic books.
For instance, the popular video game series "God of War" features a diverse cast of gods, both high and low tier, who interact in complex and often surprising ways. This modern interpretation of mythology highlights the enduring appeal of these ancient figures.
Worship and Rituals
In ancient societies, the worship of low tier gods often involved specific rituals and offerings designed to appease and honor these deities. These practices varied widely depending on the culture and the specific god being worshipped.
For example, in ancient Rome, the festival of Robigalia was held to honor Robigus, the god of grain diseases. Farmers would make offerings of bread and wine to ensure the health of their crops. Similarly, in Hinduism, the worship of local deities often involves elaborate rituals and ceremonies.
Comparison with High Tier Gods
While low tier gods may not possess the same level of power or influence as high tier gods, their roles are no less important. In fact, their closer connection to mortal affairs often makes them more relatable and accessible to ordinary people.
High tier gods, such as Zeus in Greek mythology or Odin in Norse mythology, are often depicted as all-powerful rulers of the cosmos. Their actions and decisions have far-reaching consequences that affect the lives of mortals and gods alike. In contrast, low tier gods focus on more specific domains, providing practical assistance and guidance to those in need.
Conclusion
In conclusion, low tier gods play a vital role in the pantheon of deities, contributing to the rich tapestry of stories and beliefs that have shaped human culture. While they may not command the same level of reverence as their high-tier counterparts, their influence is undeniable.
We invite you to explore the fascinating world of mythology further by reading other articles on our site. Your feedback and comments are always welcome, and we encourage you to share this article with others who may find it interesting. Together, we can continue to uncover the mysteries and wonders of the divine realm.