Remote access to Raspberry Pi over the internet has become increasingly popular among tech enthusiasts and professionals alike. It offers the flexibility to control and manage your Raspberry Pi device from anywhere in the world, making it an essential skill for anyone working with IoT or remote computing. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional developer, understanding how to securely access your Raspberry Pi remotely can significantly enhance your productivity.
With the growing demand for remote work and IoT applications, the ability to access your Raspberry Pi from the internet is no longer just a convenience—it's a necessity. This guide will walk you through the process step by step, ensuring you have all the tools and knowledge needed to set up secure and reliable remote access.
Before diving into the technical details, it's important to understand the risks and considerations involved in exposing your Raspberry Pi to the internet. Security should always be a top priority, and we'll cover best practices to ensure your device remains protected while maintaining ease of access.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Remote Access
- Why Use Remote Access?
- Security Considerations
- Methods of Remote Access
- Setting Up SSH
- Configuring Port Forwarding
- Using Dynamic DNS
- Securing Your Remote Access
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Remote Access
Remote access allows users to connect to and control a device, such as a Raspberry Pi, from another location over the internet. This technology is particularly useful for managing servers, troubleshooting systems, and accessing files or applications remotely. For Raspberry Pi users, remote access opens up a world of possibilities, enabling you to control your device from anywhere in the world.
Why Use Remote Access?
There are numerous reasons why remote access to Raspberry Pi over the internet is beneficial. Firstly, it eliminates the need to physically be present at the device's location, saving time and effort. Secondly, it allows for seamless integration with cloud services and IoT applications, enhancing the functionality of your projects. Lastly, it provides a convenient way to monitor and manage your device, ensuring it operates efficiently at all times.
Security Considerations
When setting up remote access to Raspberry Pi over the internet, security should be a primary concern. Exposing your device to the internet can make it vulnerable to unauthorized access and cyberattacks. To mitigate these risks, it's crucial to implement strong security measures such as using strong passwords, enabling encryption, and regularly updating your software.
Methods of Remote Access
There are several methods for accessing Raspberry Pi remotely, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Below, we'll explore two of the most popular methods: SSH and VNC.
SSH Remote Access
SSH (Secure Shell) is a protocol that allows secure communication between two devices over an unsecured network. It is widely used for remote access due to its strong encryption and authentication mechanisms. To use SSH for remote access to Raspberry Pi, you'll need to enable the SSH service on your device and configure your router to allow incoming connections.
VNC Remote Access
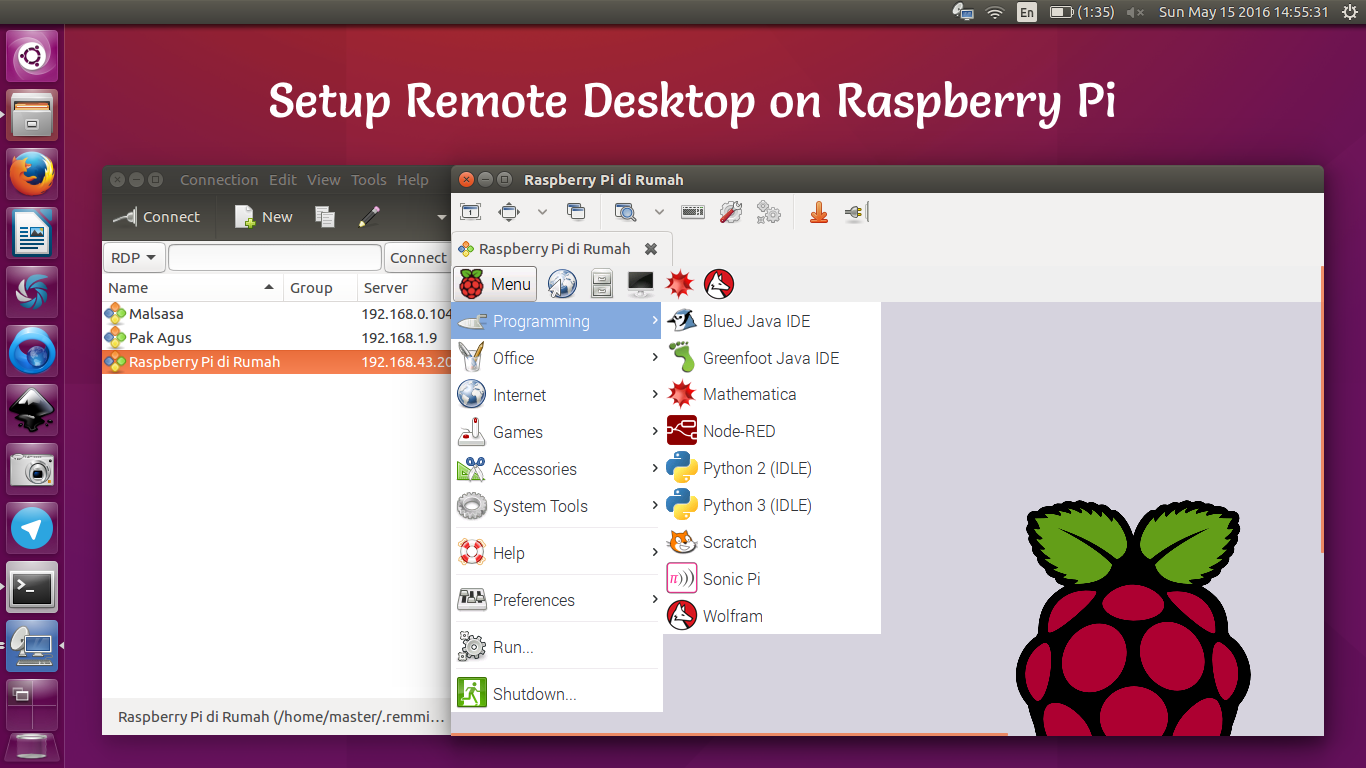
VNC (Virtual Network Computing) is a graphical desktop sharing system that allows you to remotely control another computer. Unlike SSH, which provides a command-line interface, VNC offers a full graphical interface, making it ideal for tasks that require visual interaction. Setting up VNC on Raspberry Pi involves installing a VNC server and configuring it to work with your network.
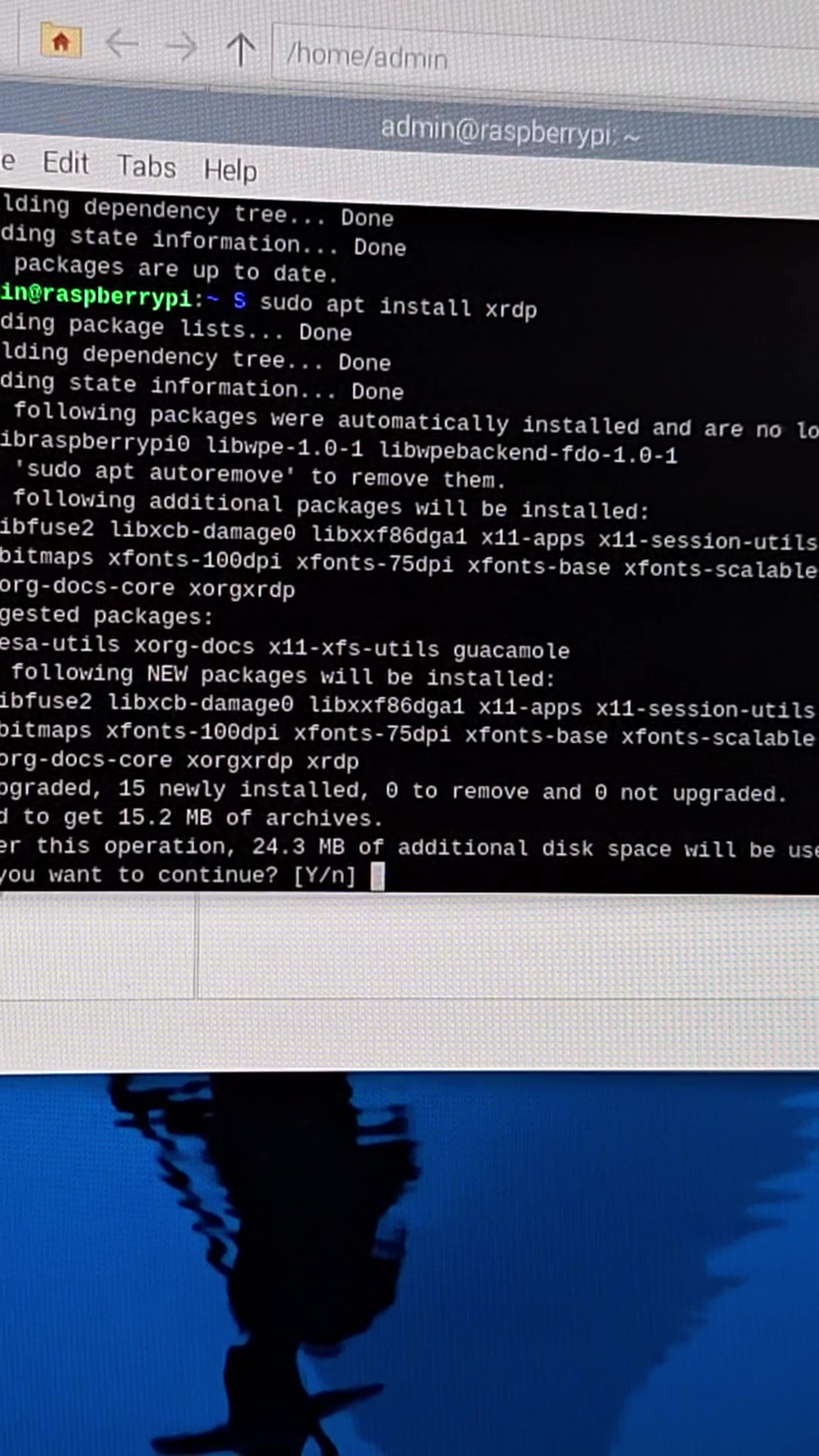
Setting Up SSH
To enable SSH on your Raspberry Pi, follow these steps:
- Connect to your Raspberry Pi using a monitor and keyboard.
- Open the terminal and type
sudo raspi-config. - Select "Interfacing Options" and enable SSH.
- Reboot your Raspberry Pi to apply the changes.
Once SSH is enabled, you can connect to your Raspberry Pi from another computer using an SSH client like PuTTY (for Windows) or the built-in terminal (for macOS and Linux).
Configuring Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is the process of forwarding a network port from one network node to another. To access your Raspberry Pi over the internet, you'll need to configure port forwarding on your router. This involves:
- Logging into your router's admin interface.
- Locating the port forwarding settings.
- Adding a new rule to forward port 22 (the default SSH port) to your Raspberry Pi's local IP address.
Make sure to note your router's public IP address, as you'll need it to connect to your Raspberry Pi from outside your local network.
Using Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a service that automatically updates your domain name to point to your router's public IP address, even if it changes. This is particularly useful if your internet service provider assigns dynamic IP addresses. To use DDNS for remote access to Raspberry Pi:
- Sign up for a DDNS service such as No-IP or DuckDNS.
- Install the DDNS client software on your router or Raspberry Pi.
- Configure the client to update your domain name whenever your IP address changes.
With DDNS set up, you can connect to your Raspberry Pi using a consistent domain name instead of an IP address.
Securing Your Remote Access
Security is paramount when setting up remote access to Raspberry Pi over the internet. Here are some best practices to keep your device safe:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
- Change the default SSH port to a non-standard port number.
- Limit access to specific IP addresses using firewall rules.
- Regularly update your Raspberry Pi's operating system and software.
By following these security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your device.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful setup, issues can arise when trying to access Raspberry Pi remotely. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Cannot connect via SSH: Ensure that SSH is enabled on your Raspberry Pi and that port forwarding is correctly configured on your router.
- Connection timeout: Check your router's public IP address and verify that it matches the address you're using to connect.
- Authentication failure: Double-check your username and password, and ensure that your SSH client is configured correctly.
If you encounter persistent issues, consult the official Raspberry Pi documentation or seek help from online forums and communities.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Remote access to Raspberry Pi over the internet is a powerful tool that can enhance your projects and streamline your workflow. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can set up secure and reliable remote access with confidence. Remember to prioritize security and regularly update your device to protect against potential threats.
We encourage you to share your experiences and tips in the comments section below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more in-depth guides on Raspberry Pi and related technologies. Together, let's build a community of knowledgeable and innovative Raspberry Pi enthusiasts!
Call to Action: If you found this article helpful, please share it with your friends and colleagues. Don't forget to subscribe to our newsletter for the latest updates and tutorials!