In today's competitive market, the concept of supply plays a crucial role in shaping business strategies and economic stability. Supply refers to the total amount of a specific good or service available to consumers. It is one of the fundamental building blocks of economics, influencing pricing, production, and market equilibrium. Understanding supply is essential for businesses, economists, and policymakers to make informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency.
Supply is not just about producing goods or services but also involves understanding consumer demand, resource allocation, and market dynamics. This article delves into the intricacies of supply, exploring its various dimensions and how it interacts with other economic factors. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of supply and its significance in modern economics.
Whether you are a business owner, student, or simply someone interested in economics, this article provides valuable insights into the world of supply. We will cover everything from the basic principles to advanced strategies, ensuring that you leave with actionable knowledge to apply in real-world scenarios.
What is Supply?
Supply, in economic terms, refers to the quantity of a product or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at various prices during a specific period. This concept is fundamental to understanding how markets function and how prices are determined. The supply curve, which illustrates the relationship between price and quantity supplied, is a critical tool used by economists to analyze market behavior.
The law of supply states that, generally, as prices rise, producers are incentivized to supply more goods or services. Conversely, when prices fall, the quantity supplied decreases. This inverse relationship between price and quantity supplied forms the backbone of supply theory and is influenced by several factors, including production costs, technology, and resource availability.
Key Factors Affecting Supply
1. Production Costs
Production costs significantly impact the supply of goods and services. When the cost of raw materials, labor, or overheads increases, producers may reduce their supply due to lower profit margins. Conversely, a decrease in production costs can lead to an increase in supply as producers find it more profitable to produce and sell their goods.
2. Technology
Technological advancements can enhance production efficiency, leading to an increase in supply. For instance, automation and digital tools have revolutionized manufacturing processes, allowing businesses to produce more goods at a lower cost. This technological edge enables producers to meet consumer demand more effectively.
3. Government Policies
Government policies, such as taxes, subsidies, and regulations, can also influence supply. Tax incentives or subsidies may encourage producers to increase their output, while stringent regulations or high taxes might discourage production. Understanding the role of government intervention is crucial for businesses operating in regulated industries.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The interaction between supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall, creating a surplus. On the other hand, when demand exceeds supply, prices rise, leading to a shortage. This delicate balance is constantly influenced by external factors such as consumer preferences, economic conditions, and global events.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their operations and maximize profits. By analyzing supply and demand trends, companies can make informed decisions regarding production levels, pricing strategies, and market entry.
Types of Supply
1. Individual Supply
Individual supply refers to the quantity of a product or service that a single producer is willing to supply at different price levels. This type of supply is often analyzed in microeconomic studies to understand the behavior of individual firms within a market.
2. Market Supply
Market supply represents the total quantity of a product or service available from all producers in a market. It is the sum of individual supplies and provides a broader perspective on the overall availability of goods or services in a specific market.
3. Joint Supply
Joint supply occurs when the production of one good automatically results in the production of another. For example, the production of beef also generates leather as a by-product. Understanding joint supply is important for industries where multiple products are derived from a single production process.
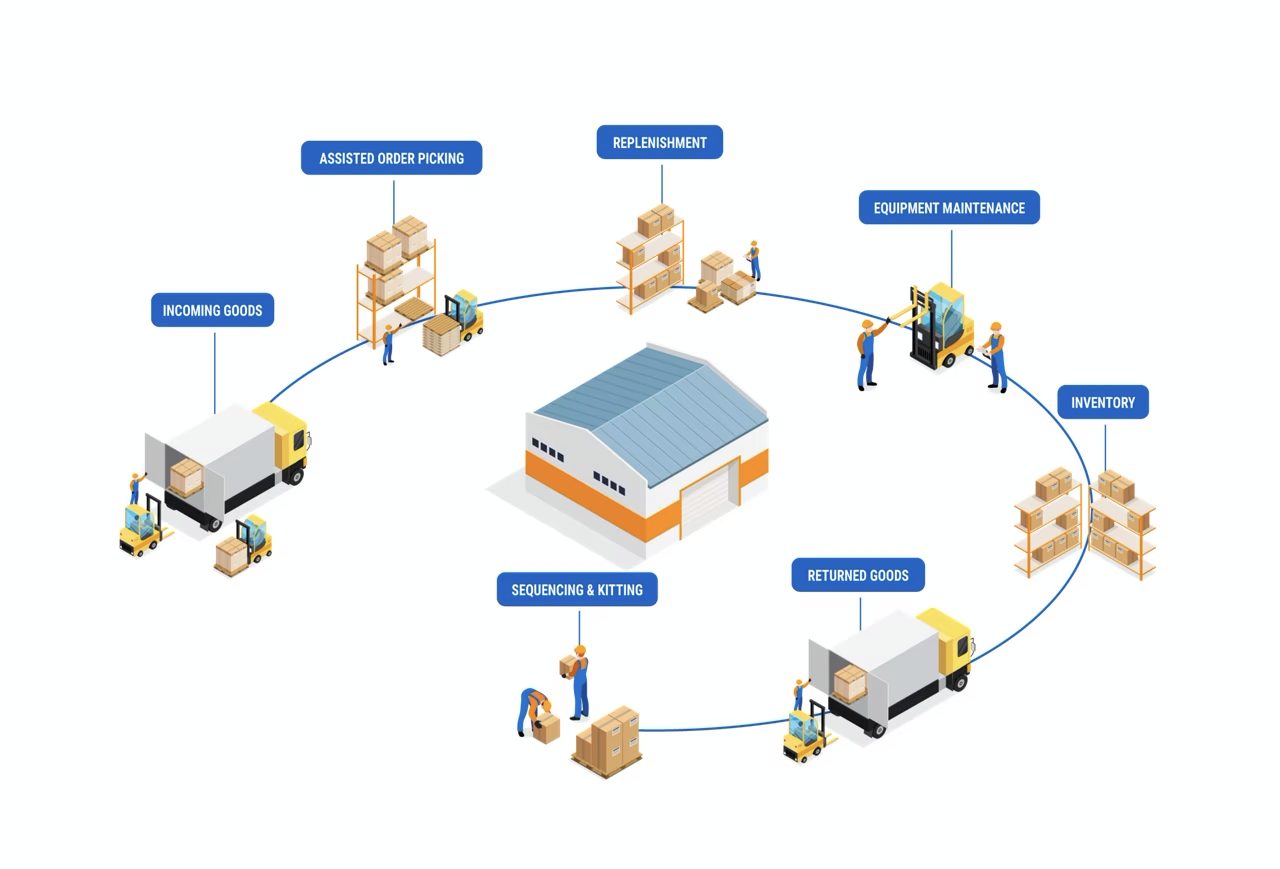
The Importance of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) is a critical aspect of modern business operations. It involves the coordination and management of all activities involved in sourcing, procurement, conversion, and logistics management. Effective SCM ensures that goods and services are delivered to customers efficiently and at the lowest possible cost.
- Optimizes inventory levels to reduce holding costs
- Improves delivery times and customer satisfaction
- Enhances collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors
Businesses that invest in robust supply chain systems can gain a competitive advantage by ensuring timely delivery, reducing costs, and improving product quality.
Challenges in Supply Management
Despite its importance, supply management faces several challenges that can hinder its effectiveness. These include:
1. Global Disruptions
Global events such as pandemics, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains, leading to delays and increased costs. Businesses must develop contingency plans to mitigate the impact of such disruptions.
2. Technological Integration
Integrating advanced technologies into supply chain operations can be complex and costly. However, the benefits of improved efficiency and accuracy often outweigh the initial investment required.
3. Sustainability Concerns
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, businesses are under pressure to adopt sustainable practices in their supply chains. This includes reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and sourcing materials responsibly.
Supply Forecasting Techniques
Accurate supply forecasting is essential for businesses to meet customer demand effectively. Several techniques are used to predict future supply needs, including:
1. Historical Data Analysis
Examining past sales data and trends can help businesses anticipate future demand patterns and adjust their supply accordingly.
2. Statistical Models
Statistical models, such as regression analysis and time-series forecasting, provide quantitative insights into supply and demand dynamics, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions.
3. Machine Learning Algorithms
Advanced machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict supply needs with greater accuracy than traditional methods.
Impact of Supply on Economic Growth
Supply is a critical driver of economic growth, influencing production levels, employment opportunities, and overall economic output. When supply increases, businesses can produce more goods and services, leading to job creation and increased GDP. However, excessive supply without corresponding demand can lead to market imbalances and economic instability.
Governments and policymakers play a vital role in ensuring that supply levels are aligned with economic needs. By implementing supportive policies and investing in infrastructure, they can create an environment conducive to sustainable growth.
Supply Chain Innovation and the Future
The future of supply chain management lies in innovation and adaptation to changing market conditions. Emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are transforming the way supply chains operate, offering new opportunities for efficiency and transparency.
Businesses that embrace these innovations will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of global markets and meet the evolving needs of consumers.
Conclusion
Supply is a cornerstone of modern economics, influencing everything from business operations to global trade. By understanding the factors that affect supply and the dynamics of supply and demand, businesses can make informed decisions that drive growth and success. Effective supply chain management, accurate forecasting, and innovative practices are key to staying competitive in today's fast-paced market.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Have you encountered any unique challenges in supply management? How have you addressed them? Additionally, explore our other articles for more insights into economics and business strategies. Together, let's build a better understanding of the world of supply and its impact on our lives.
Table of Contents
- What is Supply?
- Key Factors Affecting Supply
- Supply and Demand Dynamics
- Types of Supply
- The Importance of Supply Chain Management
- Challenges in Supply Management
- Supply Forecasting Techniques
- Impact of Supply on Economic Growth
- Supply Chain Innovation and the Future
- Conclusion
Data and insights in this article are supported by credible sources such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Trade Organization (WTO), and academic publications on economics. For further reading, we recommend exploring these resources to deepen your understanding of supply and its role in shaping the global economy.

![[Infographic] What is supply chain management? Logistics](https://mexicomlogistics.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/definition-supply-chain-management.png)